Fact Sheet: Asylum in the United States
(PRESS RELEASE) Each year, thousands of noncitizens arriving at our border or already in the United States apply for asylum, or protection from persecution. Asylum seekers must navigate a difficult and complex process that can involve multiple government agencies. Those granted asylum have the opportunity to apply to live in the United States permanently, receive certain benefits, and be reunited with their family members. This fact sheet provides an overview of the asylum system in the United States, including how asylum is defined, eligibility requirements, and the application process.
What Is Asylum?
Asylum is a protection granted to foreign nationals already in the United States or at the border who meet the international law definition of a “refugee.” The United Nations 1951 Convention and 1967 Protocol define a refugee as a person who is unable or unwilling to return to his or her home country, and cannot obtain protection in that country, due to past persecution or a well-founded fear of being persecuted in the future “on account of race, religion, nationality, membership in a particular social group, or political opinion.” Congress incorporated this definition into U.S. immigration law in the Refugee Act of 1980.
As a signatory to the 1967 Protocol, and through U.S. immigration law, the United States has legal obligations to provide protection to those who qualify as refugees. The Refugee Act established two paths to obtain refugee status—either from abroad as a resettled refugee or in the United States as an asylum seeker.
What Are the Benefits of Asylum?
An asylee—or a person granted asylum—is protected from being returned to his or her home country, is authorized to work in the United States, may apply for a Social Security card, may request permission to travel overseas, and can petition to bring family members to the United States. Asylees may also be eligible certain benefits, such as Medicaid or Refugee Medical Assistance.
After one year, an asylee may apply for lawful permanent resident status (i.e., a green card). Once the individual becomes a permanent resident, he or she must wait four years to apply for citizenship.
What Is the Asylum Application Process?
There are two primary ways in which a person may apply for asylum in the United States: the affirmative process and the defensive process. Asylum seekers who arrive at a U.S. port of entry or enter the United States without inspection generally must apply through the defensive asylum process. Both processes require the asylum seeker to be physically present in the United States.
- Affirmative Asylum: A person who is not in removal proceedings may affirmatively apply for asylum through U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), a division of the Department of Homeland Security (DHS). If the USCIS asylum officer does not grant the asylum application and the applicant does not have a lawful immigration status, he or she is referred to the immigration court for removal proceedings, where he or she may renew the request for asylum through the defensive process and appear before an immigration judge.
- Defensive Asylum: A person who is in removal proceedings may apply for asylum defensively by filing the application with an immigration judge at the Executive Office for Immigration Review (EOIR) in the Department of Justice. In other words, asylum is applied for “as a defense against removal from the U.S.” Unlike the criminal court system, EOIR does not provide appointed counsel for individuals in immigration court, even if they are unable to retain an attorney on their own.
With or without counsel, an asylum seeker has the burden of proving that he or she meets the definition of a refugee. Asylum seekers often provide substantial evidence throughout the affirmative and defensive processes demonstrating either past persecution or that they have a “well-founded fear” of future persecution in their home country. However, the individual’s own testimony is usually critical to his or her asylum determination.
Certain factors bar individuals from asylum. With limited exceptions, individuals who fail to apply for asylum within one year of entering the United States will be barred from receiving asylum. Similarly, applicants who are found to pose a danger to the United States are barred from asylum.
Is There a Deadline for Asylum Applications?
An individual generally must apply for asylum within one year of arriving in the United States. Whether DHS is obligated to notify asylum seekers of this deadline is the subject of pending litigation. A class-action lawsuit has challenged the government’s failure to provide asylum seekers adequate notice of the one-year deadline and a uniform procedure for filing timely applications.
Asylum seekers in the affirmative and defensive processes face many obstacles to meeting the one-year deadline. Some individuals face traumatic repercussions from their time in detention or journeying to the United States and may never know that a deadline exists. Even those who are aware of the deadline encounter systemic barriers, such as lengthy backlogs, that can make it impossible to file their application in a timely manner. In many cases, missing the one-year deadline is the sole reason the government denies an asylum application.
What Happens to Asylum Seekers Arriving at a U.S. Border?
Noncitizens who are encountered by, or present themselves to, a U.S. official at a port of entry or near the border are subject to expedited removal, an accelerated process which authorizes DHS to perform rapid deportations of certain individuals.
To ensure that the United States does not violate international and domestic laws by returning individuals to countries where their life or liberty may be at risk, the credible fear and reasonable fear screening processes are available to asylum seekers in expedited removal processes.
Credible Fear
Individuals who are placed in expedited removal proceedings and who tell a Customs and Border Protection (CBP) official that they fear persecution, torture, or returning to their country or that they wish to apply for asylum should be referred for a credible fear screening interview conducted by an asylum officer.
If the asylum officer determines that the asylum seeker has a credible fear of persecution or torture, it means that the person has proven that he or she has a “significant possibility” of establishing eligibility for asylum or other protection under the Convention Against Torture. The individual will then be referred to immigration court to proceed with the defensive asylum application process.
If the asylum officer determines the person does not have a credible fear, the individual is ordered removed. Before deportation, the individual may appeal the negative credible fear decision by pursuing a truncated review process before an immigration judge. If the immigration judge overturns a negative credible fear finding, the individual is placed in further removal proceedings through which the individual can seek protection from removal. If the immigration judge upholds the negative finding by the asylum officer, the individual will be removed from the United States.
- In Fiscal Year (FY) 2017, USCIS found 60,566 individuals to have credible fear. These individuals, many of whom were detained during this screening process, will be afforded an opportunity to apply for asylum defensively and establish that they meet the refugee definition.
- The number of credible fear cases has skyrocketed since the procedure was implemented—in FY 2009, USCIS completed 5,523 cases. Case completions reached an all-time high in FY 2016 at 92,071 and decreased to 79,977 in FY 2017.
Reasonable Fear
Individuals who re-enter the United States unlawfully after a prior deportation order and noncitizens convicted of certain crimes are subject to a different expedited removal process called reinstatement of removal. To protect asylum seekers from summary removal before their asylum claim is heard, those in reinstatement of removal proceedings who express a fear of returning to their country are afforded a “reasonable fear” interview with an asylum officer.
To demonstrate a reasonable fear, the individual must show that there is a “reasonable possibility” that he or she will be tortured in the country of removal or persecuted on the basis of race, religion, nationality, political opinion, or membership in a particular social group. While both credible and reasonable fear determinations evaluate the likelihood of an individual’s persecution or torture if deported, the reasonable fear standard is higher.
If the asylum officer finds that the person has a reasonable fear of persecution or torture, he or she will be referred to immigration court. The person has the opportunity to prove to an immigration judge that he or she is eligible for “withholding of removal” or “deferral of removal”—protection from future persecution or torture. While withholding of removal is similar to asylum, some of the requirements are more difficult to meet and the relief it provides is narrower. Significantly, and unlike asylum, it does not provide a pathway to lawful permanent residence.
If the asylum officer determines the person does not have a reasonable fear of future persecution or torture, the individual may appeal the negative decision to an immigration judge. If the judge upholds the asylum officer’s negative determination, the individual is turned over to immigration enforcement officers for removal. However, if the immigration judge overturns the asylum officer’s negative finding, the individual is placed in removal proceedings through which the individual can pursue protection from removal.
- In FY 2017, USCIS found 3,018 individuals to have reasonable fear.
How Long Does the Asylum Process Take?
Overall, the asylum process can take years to conclude. In some cases, a person may file his or her application and receive a hearing or interview date years in the future.
- As of March 2018, there were more than 318,000 affirmative asylum applications pending with USCIS. The government does not estimate the time it will take to schedule an initial interview for these asylum applicants, though historically the delay could reach four years for such asylum seekers.
- The backlog in U.S. immigration courts reached an all-time high in March 2018 with more than 690,000 open deportation cases. On average, these cases had been pending for 718 days and remained unresolved.
- Individuals with an immigration court case who were ultimately granted relief—such as asylum—by March 2018 waited more than 1,000 days on average for that outcome. New Jersey and California had the longest wait times, averaging 1,300 days until relief was granted in the immigration case.
Asylum seekers, and any family members waiting to join them, are left in limbo while their case is pending. The backlogs and delays can cause prolonged separation of refugee families, leave family members abroad in dangerous situations, and make it more difficult to retain pro bono counsel for the duration of the asylum seeker’s case.
Although asylum seekers may apply for work authorization after their case has been pending for 150 days, the uncertainty of their future impedes employment, education, and trauma recovery opportunities.
What Happens to Asylum Seekers While Their Application Is Processed?
Asylum seekers include some of the most vulnerable members of society—children, single mothers, victims of domestic violence or torture, and other individuals who have suffered persecution and trauma. Some of these individuals may live in the United States while their application is processed, yet the government has detained others—including children and families—for some or all of this time.
While U.S. law provides arriving asylum seekers the right to be in the United States while their claim for protection is pending, the government has argued that it has the right to detain such individuals. Some courts have rejected this interpretation and held that asylum seekers meeting certain criteria have a right to a hearing over their detention if they have been held for at least six months. Several lawsuits have challenged the practice of detaining asylum applicants, including class-action suits that document the prolonged detention—sometimes lasting years—of individuals with credible fear awaiting adjudication of their claim for asylum.
Detention exacerbates the challenges asylum seekers already face and can negatively impact a person’s asylum application. Children and families who are detained suffer mental and physical health problems, including depression, post-traumatic stress disorder, and frequent infections. Studies have found that detained individuals in removal proceedings are nearly five times less likely to secure legal counsel than those not in detention. This disparity can significantly affect an individual’s case, as those with representation are more likely to apply for protection in the first place and successfully obtain the relief sought.
How Many People Are Granted Asylum?
In FY 2016, the most recent year with available data, 20,455 individuals were granted asylum: 11,729 affirmatively and 8,726 defensively (Figure 1). Total annual asylum grants averaged 23,669 between FY 2007 and FY 2016.
Figure 1: Individuals Granted Asylum Affirmatively or Defensively: Fiscal Years 1990 to 2016
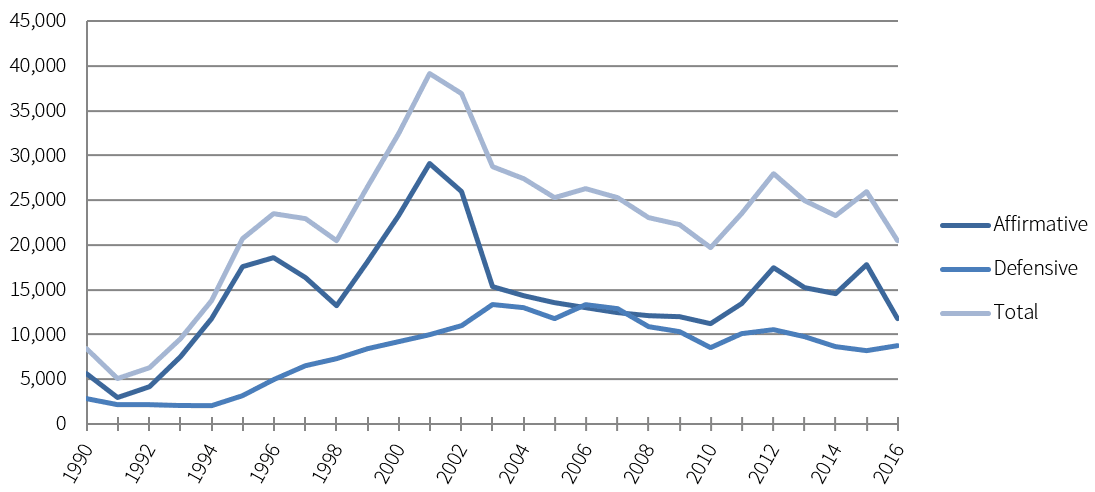
Source: Office of Immigration Statistics, Table 16 in 2016 Yearbook of Immigration Statistic (Washington, DC: U.S. Dep’t of Homeland Sec., 2018), https://www.dhs.gov/immigration-statistics/yearbook/2016/table16.
The countries of nationality for individuals granted asylum have largely remained the same in this 10-year period (FY 2007-2016), with nationals of China and Egypt making up significant shares of asylees. Other individuals granted asylum in that time period included nationals of Guatemala, Haiti, Venezuela, Iraq, Ethiopia, Iran, Colombia, and Russia.
In FY 2016, Chinese and Salvadoran nationals represented the greatest shares of asylees (accounting for 21.9 and 10.5 percent, respectively, of all individuals granted asylum in FY 2016). Nationals of China, El Salvador, Guatemala, and Honduras combined accounted for half (49.4 percent) of the 20,455 individuals granted asylum—either affirmatively or defensively—in FY 2016 (Figure 2). A total of 98 nationalities were represented among all individuals granted asylum in FY 2016.
Figure 2: Total Asylum Grants by Country of Nationality, Fiscal Year 2016

* Includes the Palestinian Territory and countries with less than 10 individuals granted asylum in FY 2016.
Source: American Immigration Council analysis of government data. Office of Immigration Statistics, Tables 17 and 19 in 2016 Yearbook of Immigration Statistic (Washington, DC: U.S. Dep’t of Homeland Sec., 2018), https://www.dhs.gov/immigration-statistics/yearbook/2016.





